In Data Modelling Infrastructure there are five modelling techniques that are:
In this type of Data Modelling Infrastructure database model, data is organised in a tree-like structure. It has only one root node. Each record has only a single root/parent node. This model usually describes real-world relationships.
Key Points:
-
-
- Nested Model
- Multilevel models
-

[2] Object-Oriented Model
The data is considered as a collection of objects where objects are real-world things in this database model.
Key Points:
-
-
- the base for JDBC, ODBC
-
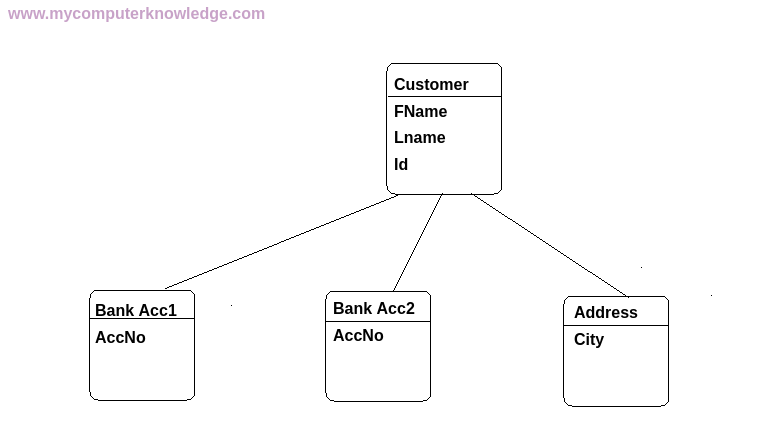
[3] Network Model
In Network model, the data is stored in form of a graph. Here a single child node may have two or more parent nodes. Making a graph-like structure. It is useful in showing the Many-to-Many relationship between data.
Key Points:
-
-
- Can represent Many-to-Many relationship
- Multilevel graph-like structure
-

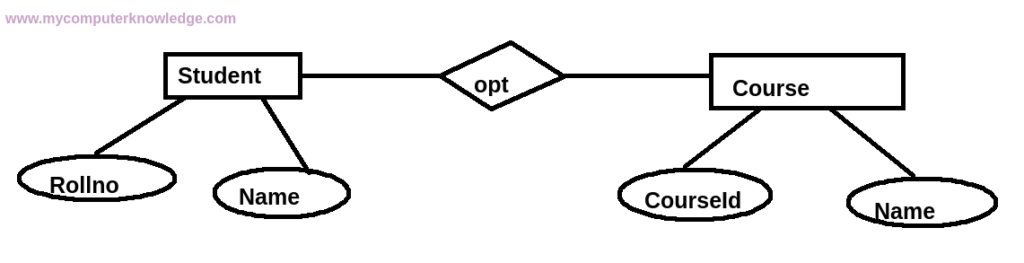
[4] Entity-Relationship Model
In this database model, the data is composed of entities, that can be any real-world thing and the relationship shows how the entities are related to each other.
Key Points:
-
-
- Helps in visualisation for the stakeholders
- Forms base for Relational model
-
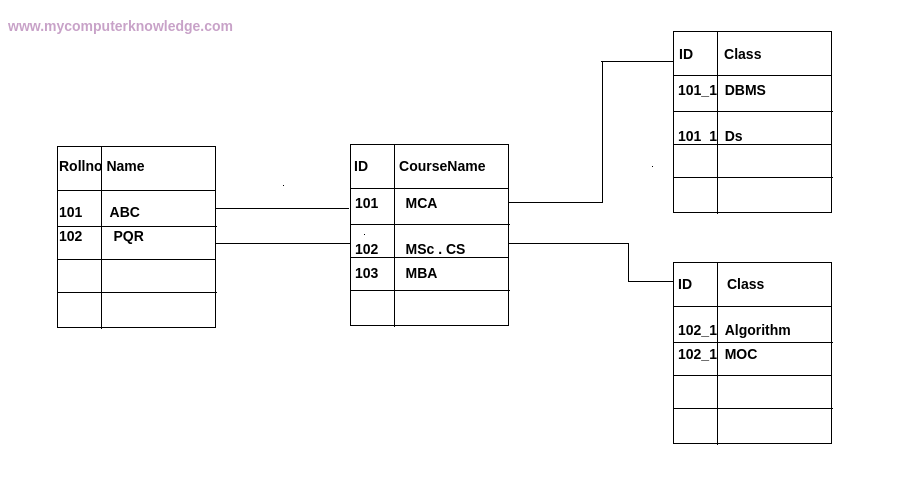
[5] Relational Model
In this database model, the data is organised in form of tables. Tables are known as relations. Each table has rows and columns. Columns are the attributes. All these attributes make domain. A set of attributes or a single attribute can be the primary key, i.e. the unique identifier of the table.
Key Points:
-
-
- Tables can be normalised
- Relational databases are written in SQL(Structured query language)
-
If you like the post Data Modelling Infrastructure, please share your feedback!
also see
| C Programming language |
Go Programming language |
| Linked List | Array |
| Simplification | Queue |
| DBMS | Reasoning |
| Aptitude | HTML |






































